A stakeholder is any individual, a group of people or an organization who can affect or be affected positively or negatively by the project.
Stakeholders are simply those who have a particular direct or indirect interest in a project or result. Remember, not all stakeholders have the same interest in the project.
The stakeholders can be;
- individuals within the project like Project team
- individuals or departments within the organization &
- individuals or groups outside the organization like influencers, outside consultants
In this article, we will discuss the Management & Engagement of Stakeholders. Though to manage stakeholders is something “Disrespectful” to the owners and we will mainly focus on Engagement of the stakeholders.
How to Manage/Engage Stakeholder?
As we know, a stakeholder can be in favour of your project and we call it positive stakeholder and also it can be a negative stakeholder that is against your project. Hence, the proper management of stakeholders is really important for a successful project.
We use a different set of techniques that harnesses the positive effect and minimizes the effect of negative influences. It comprises below main steps;
- Identify Stakeholders
- Analyze their Interest and Influence
- Develop Communication Management Plans
- Engage and Influence stakeholders
To identify stakeholders is a very important process that helps to manage and engage them. Make sure this process of identifying stakeholders is throughout the project life cycle and as their interests, influence, and impact may change during the course of the project. Following are the benefits to identify stakeholders but not limited to;
- It will improve the quality of the project
- It will help to avoid delays
- It will help you to get extra support during the life cycle of a project.
Before going for applying tools and techniques for identification of project stakeholders first make sure to get the answer to these questions with you like who;
- is indirectly involved with the project?
- maybe affected by the project?
- maybe affected by the project’s outcome?
- are the competitors?
- are the shareholders?
- is affected positively and negatively by the project?
- has the power to make it succeed (or fail)?
- makes the decisions about money?
- are the suppliers?
- are the end-users?
- has influence over other stakeholders?
- could solve potential problems with the project?
- is in charge of assigning or procuring resources or facilities?
- has specialist skills which are crucial to the project?
- gains or losses from the project’s success?
- wants to complete the project successfully and who doesn’t?
- is the user of the result of the project?
- has the authority to influence the project or its outcome?
- has the authority to make the project succeed?
Inputs for Identity Stakeholders
Following documents can help you to identify stakeholders on any particular project;
Project Charter: It is a High-level document that authorizes the project to the project manager
Procurement Documents: Help to Identify procurement contract stakeholders
Enterprise Environmental Factors: Consideration factors such as culture, systems, procedures, industry standards
Organizational Process Assets: Consider factors such as templates, lessons learned, stakeholder registers.
Tools & Techniques to Identify Stakeholders
Stakeholder Analysis: Gathering and assessing information to determine whose interests should be taken into account
Expert Judgment: Expert technical and/or managerial judgment
Output of Identity Stakeholders
We will get the following Outputs;
Stakeholder Register A document identifying all project stakeholder information, requirements, and classification
Stakeholder Management Strategy: Defines the approach to increase stakeholder support and reduce negative impacts represented in a stakeholder analysis matrix
Now we will see types of stakeholders to further know about these.
Type of Project Stakeholders
Commonly stakeholders are categorized as below:
- Internal & External Stakeholders
- Primary, Secondary & Tertiary Stakeholders
- Voluntary vs. Involuntary Stakeholders
But if you are going for PMI-PMP then you only need to consider Internal & External stakeholders
Internal & External Stakeholders
This one the most simple classification of project stakeholders. You can easily understand from the following diagram.
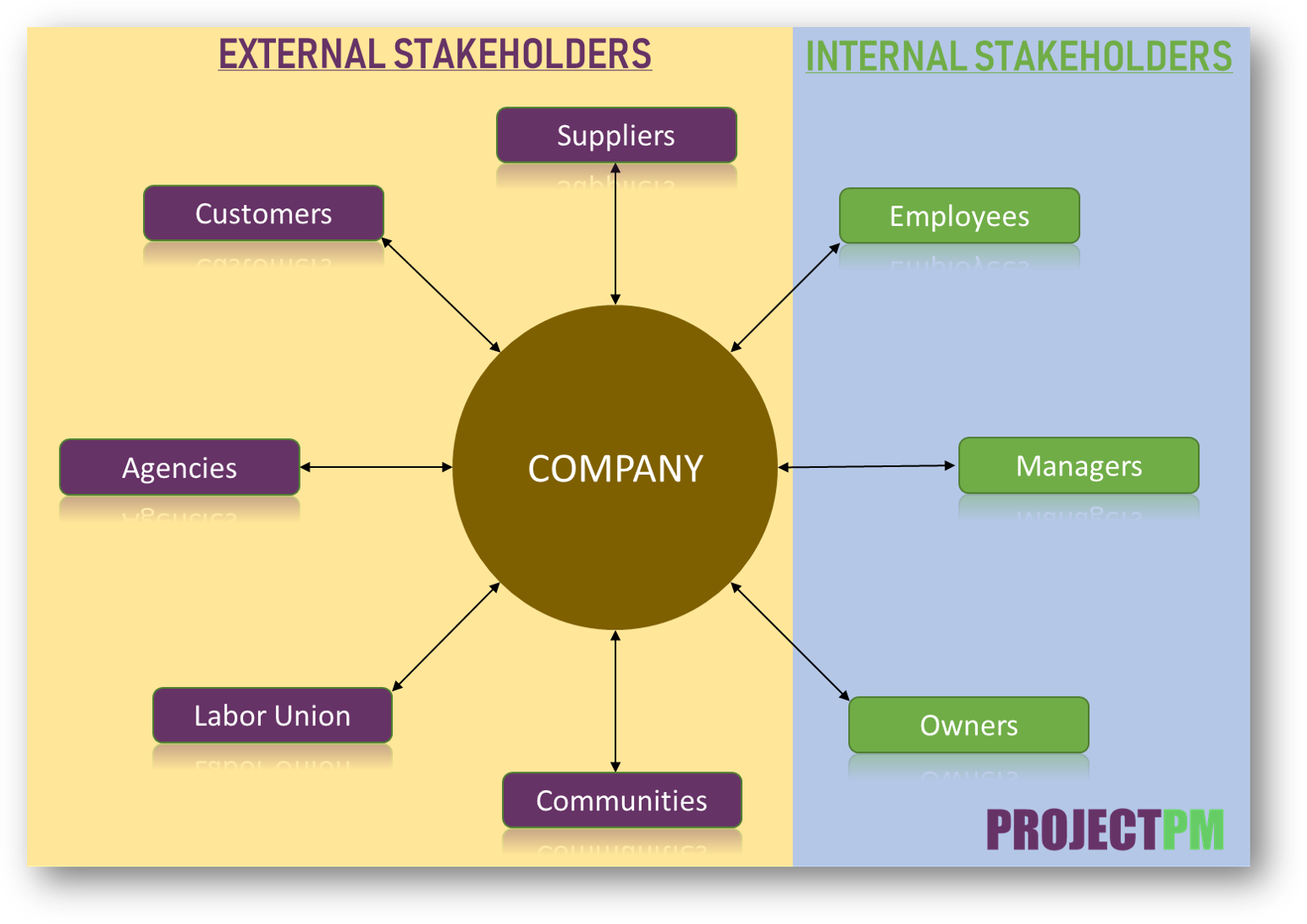
Internal Stakeholders
Internal stakeholders are internal to the organization. Let see stakeholders examples with types of stakeholders;
- A sponsor/owner
- Employees
- Board of Directors
- Investors:
- A project team
- A program manager
- A portfolio manager
- Management
- Another group’s manager internal to the organization
- An internal customer or client
External Stakeholders
These stakeholders are external to the organization. For example:
- Customers
- Creditors
- Society
- Government
- Any external client
- An end-user
- Suppliers
- Subcontractors
- The government
- Local communities
- The media
- Intermediaries
- Competitors
Key Differences
To make things easy make sure to know the key difference between internal and external stakeholders;
- Internal Stakeholders are meant to serve the organisation,
- External Stakeholders always deal with the company from an outside party.
- Internal Stakeholders are influenced directly by the activities.
- Internal Stakeholders are direct employees of the company.
- Internal stakeholders must aware of the internal matters of the company.
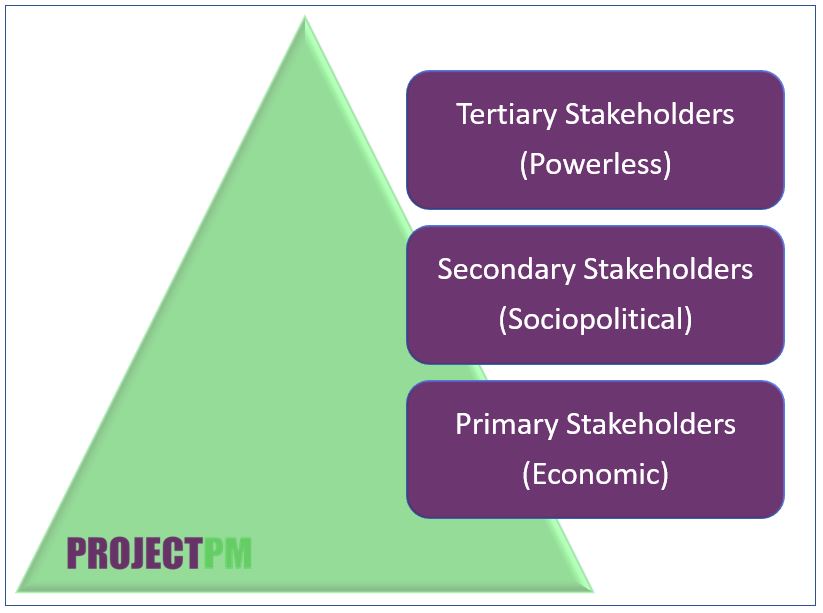
Stakeholders Model
Some school of thought classify by this. Primary, secondary and tertiary classified definitions are the most common. We do this to identify and to understand better the stakeholders on our project. Whatever classification you do, always keep in mind that the Internal Stakeholders are the primary stakeholders whereas External stakeholders are the secondary stakeholders or even tertiary.
Let see briefly about these ones by one;
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary Stakeholders
Primary Stakeholders Model
There are five different primary stakeholders.
- Stockholders
- Customers
- Employees
- Government
- Communities
Secondary Stakeholders Model
There are five different secondary stakeholders as well.
- The Media
- Activists
- Competitors
- Management
- The Board of Directors
Tertiary Stakeholders Model
There are six tertiary stakeholders.
- The Unions
- Political Groups
- Business Community
- Universities
- The Courts
- Suppliers
You can see below pyramid to understand their authority on any project.
How to Analyse stakeholders?
This classification will make things easy when managing and engaging the stakeholders as we know their stakes well after careful analysis.
Stakeholders analysis is a process that involves identifying all potential stakeholders, finding their needs and level of interest or influence.
There are five techniques used for Stakeholder Analysis.
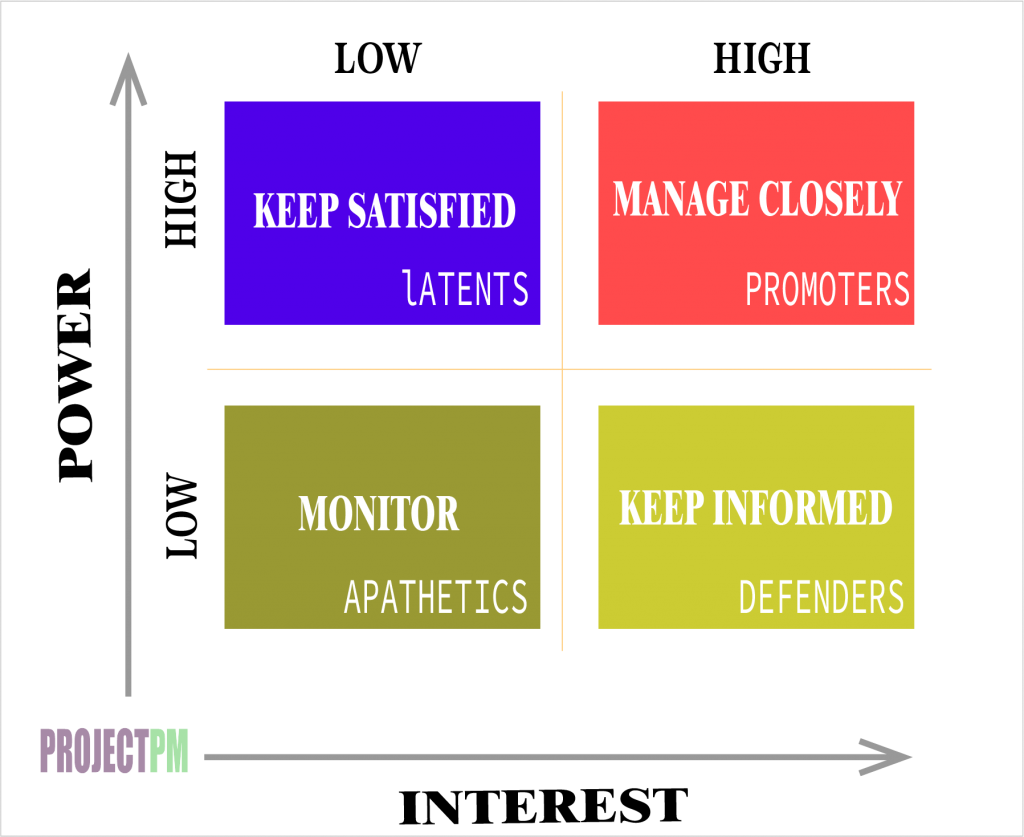
Power vs Interest Grid
This is the most important grid as we use the power of a stakeholder to manage and engage. Let’s go through this stakeholder analysis technique with the help of the following figure.
High Power | High Interest
You need to engage that guy in all respects regularly. These are actually the key players in your project. Always make sure to keep this group satisfied with level up to date information…
High Power | Low Interest
They need not overloaded by the information on your project. They need specific and concise reporting, not a detailed analysis.
Low Power | High Interest
This group should be kept adequately informed. You can consult with them regarding their area of interest.
Low Power | Low Interest
This group includes stakeholders which only require general information. Don’t overload them and just put in under your radar/umbrella all the time.
Influence Impact Grid
In this stakeholder analysis technique, we use Influence & Impact grid that is quite similar to Power & interest.
- An influence versus impact grid we plot
- It helps to prioritize stakeholders
Power Influence Grid
In this stakeholder analysis technique, we use power influence grid.
- It is also similar to the Power vs Interest grid.
- It helps to puta stakeholder as per activeness and authority
Importance Influence Grid
In this stakeholder analysis technique, we use the importance vs influence grid.
- It is also similar to the Power vs Interest grid.
- Here we categorize the importance and level of “Authority”
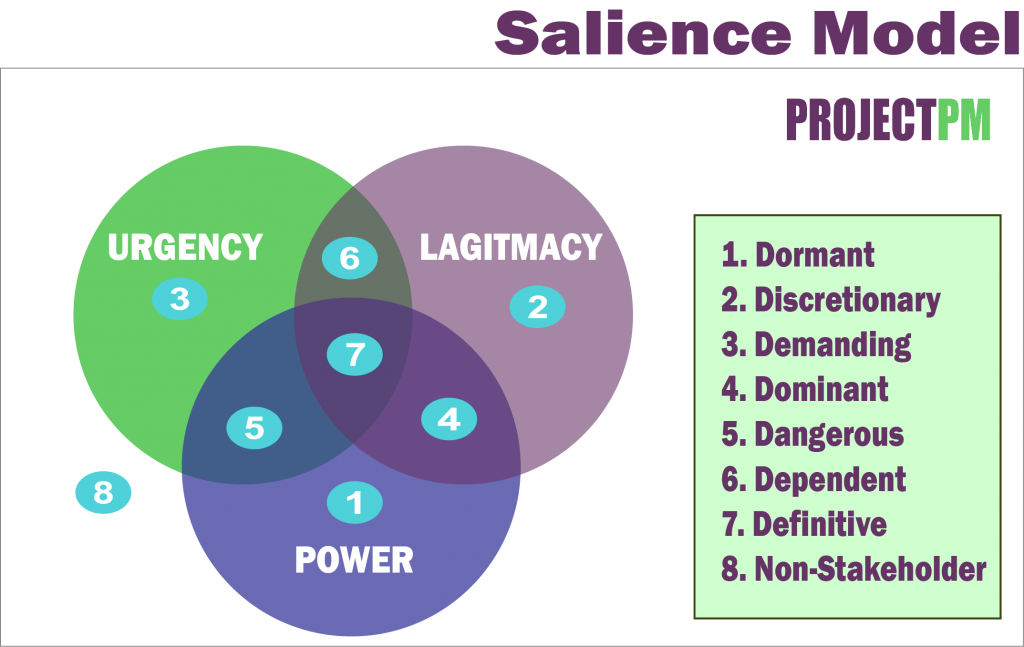
Salience Model
This is a bit different from others we just discussed. Here we use;
of stakeholders on our project.
We draw a three-dimensional model called Venn diagram and see the intersections as you see on the below figure.
Here, Urgency indicates the Project Manager that how quickly a stakeholder’s needs are to be informed or addressed.
The urgency tells the PM the importance of the stakeholder need is to the project goals. Salience is prominence in simple words. The bigger the value of factors the stakeholder has, higher is the salience or prominence.
Let us see what these are:
- Dormant: High power but no legitimacy or urgency.
- Discretionary: Rightful stakeholders but do not have urgency or power.
- Demanding: Neither power nor the legitimacy
- Dominant: Both power and legitimacy but not the urgency.
- Dangerous: Have both power and urgency.
- Dependent: Has urgency and are part of the project but do not have the power.
- Definitive: Have all three factors and hence highest salience.
- Non – Stakeholder: No concern with the project.
A careful stakeholder analysis will help a project to identify:
- Interests of overall stakeholders
- Potential issues that could disturb the project
- Key people to engage with information during the executing phase
- Communication planning & stakeholder management strategy during the project life cycle.
- Helps to manage negative stakeholders on your project
Develop Communication Management Plans
Once you’ve prioritised your stakeholders, you can then start to develop a communication plan to make sure how you are going to give information to the right person at the right time. A communication plan definitely is going to play a vital role in success & failure of any project.
There are lots of ways you can communicate channels you can communicate with stakeholders. These include:
- Meetings
- Presentations
- Project Status Reports
- Letters – Mails
- E-mails
- Website
- Newsletters
How and when to use the above method will decide as per your categorization as per stakeholders analysis.
Here, I have some tips better communicate with your project stakeholders;
- Messages should be clear, concise and at right time to the right person
- Open and honest reports are always welcome to build trust among each other.
- Don’t hide any news in addressing key concerns.
- Respect the norms and make sure to follow the multicultural environment.
- Don’t flood with unnecessary information to others just to show that how much you are doing on the project.
Engage and Influence stakeholders.
As already said that as the stakeholders are your peers and the owners and hence a proper Engagement rather than management of them is highly appreciable as a project manager. They are not all your followers and hence should be treated respectfully.
Being a project manager it is your utmost duty to engage them throughout the project life cycle and remember that only a single stakeholder can ruin the whole project.
Active involvement of stakeholders is very much important to project as:
- It creates a sense of responsibility and accountability
- It gives the opportunity to others to express their ideas, issues, concerns.
- It enables effective risk assessment and response planning
- It creates learning opportunities among stakeholders.
Once everything is done then make sure to prepare a RACI Chart that will help to further engagement among stakeholders.
Shareholder – who owns an equity stock in the company
Stakeholder – who is an interested party in company performance other than capital
A shareholder is the owner of a part through shares of stock, while any stakeholder will have an interest in the performance of a company for reasons other than stock performance or appreciation.
A shareholder is also known as a stockholder.

In 1988, Edward Freeman introduced Stakeholder theory. This theory maximizes shareholders’ interests in a way that is still permitted by law or social values. The reason for why are shareholders important stakeholders is that as they own the company through capital investment.
Differences in shareholders, stockholders, and stakeholders:
- Shareholders/stockholders must have financial shares in the organization, but the stakeholders must have an interest in the organization’s financial matters or not at all
- Shareholders are stakeholders, but all stakeholders are not part of the shareholders.
- Shareholders will be directly affected by what happens to the company, while stakeholders can be affected indirectly or directly.
- Stakeholders shares responsibilities and influence on what happens to the company, while shareholders are only affected.
- Shareholders own part of the company, while all stakeholders do not all have a part of the company.
Wrap up
A proper plan stakeholder management with a complete list of stakeholders will definitely a must-have document for engaging all project stakeholder. Stakeholders actually share business and values with each other even if you are dealing employees as stakeholders or the shareholders you must go for a win-win strategy. Stakeholder engagement strategy should be simple as everyone involved must have buy-in. Always make sure to understand the types of stakeholders you are dealing with as soon as possible.
One Small Request:
I understand life is busy when you work especially in the Project Management field. We really have no time to play around the internet. I only can request you share this information to other colleagues. It will help me to grow my blog and can reach to more people. Thank you for visiting.